IFN maintains point of presences (PoPs) for carrier interconnection (NNI) at the following locations:
- Chicago Data Center (5th flr Equinix IFN cage/2nd flr Equinix MMR), 350 East Cermak Road 5th Floor, Chicago, IL 60616
- Lifeline Data Center (basement panel/1st flr MMR/2nd flr IFN cage), 733 W Henry Street, Indianapolis, IN 46225
- Lifeline Data Center (data center MMR cage), 401 N Shadeland Avenue, Indianapolis, IN 46219
- Indy Telecom Center (valve room OCEF, garage door OCEF), 701 W Henry Street, Indianapolis, IN 46225
- OnLine Tech Data Center (carrier MMR cage), 505 W Merrill Street, Indianapolis, IN 46225
To initiate an interconnection Network-to-network interface (NNI) with IFN, contact an IFN Carrier Wholesale representative who will assign your request to an IFN project manager to guide you through the process.
The IFN Project Manager will email you a NNI Interconnection form which will gather the initial information about your company including provisioning and outside plant contact phone numbers and emails. Conference calls with the appropriate contacts from both companies will be setup to determine:
- Which location will be preferred for the interconnection NNI. During this call there will be a review of where physical facilities exist today, and monthly and non-recurring cross-connect charges for each potential interconnect location.
- Pending and expected usage will be discussed, along with a review of NNI connection costs and any other requirements.
- Based on the findings in the initial calls, the initial bandwidth for the interconnection NNI (1G/10G/100G), can be determined and what upgrades may be planned for the future.
- An interconnect agreement may be required to determine contractual usage of the NNI, assignment of CFA based on direction, and any other provisioning issues.
- Once location and logical connection arrangements are finalized, your outside plant person will be contacted to provide the physical connectivity details, and your provisioning contact will be asked to provide CFA at the selected interconnect location. The testing of the NNI interface can then be scheduled.
- This entire process may take up to 60 days to complete.
How does IFN measure usage on Burstable Internet service?
Burstable Internet is a method of measuring bandwidth based on peak utilization. It also allows usage to exceed a specified threshold for brief periods of time without the financial penalty of purchasing a higher access speed.
IFN uses a five minute sampling and 95% percentile method when calculating usage.
The 95th percentile is a widely used mathematical calculation to evaluate sustained utilization of a network connection. Bandwidth is measured (or sampled) from the switch or router and recorded in a log file. This is done every 5 minutes. At the end of the month, the samples are sorted from highest to lowest, and the top 5% (which equal to approximately 36 hours of a 30-day billing cycle) of data is thrown away. The next highest measurement becomes the billable utilization for the month.
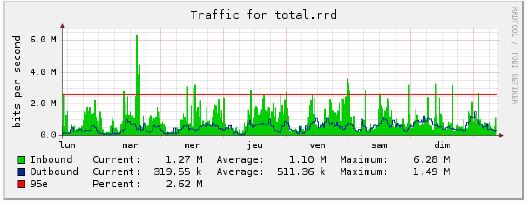
The sampling interval, or how often samples are taken, is an important factor in percentile calculation. A percentile is calculated on a set of data points. Every data point represents the average bandwidth used during the sampling interval (e.g., five minutes) and is calculated as the number of bits transferred throughout the interval divided by the duration of the interval (e.g., 300 seconds). The resulting value represents the average utilization rate for a single sampling interval and is expressed as bits per second.
How does IFN work with or support BGP Communities?
BGP Communities are a way for a customer to “Tag an IP Prefix” with a certain value that IFN’s Internet routers will then act upon. The following is a list of the BGP communities that our BGP customers may use. From a syntax stand-point, IFN does not provide any example configurations. Depending on the customer router being deployed, syntax will vary.
IFN BGP Communities
IFN has in place a mechanism that will allow BGP customers to stop DDOS traffic from entering their network through an IP “black hole” process. The requirements for turning on black-hole filtering are as follows:
- You must know the target address of the DDOS attack. In other words, you need the IP address on your network that is the target of the attack.
- You may only black-hole an /32 host prefix. This is to protect the customer from inadvertently black-holing a large part of their network. The IFN will ignore any black-hole requests for prefixes smaller than /32s.
- The /32 prefix must be sent to IFN with the BGP Community of 32703:60000.
- Once this community is sent, traffic for the /32 will immediately be dropped on the IFN core network.
- To withdrawal the black-hole request you simply remove the 32703:60000 community attribute from the prefix.
Other Communities of interest:
| Community | Description |
|---|---|
| 32703:30001 | Prepend IFN’s AS (32703) to all upstream peers ONE time. |
| 32703:30002 | Prepend IFN’s AS (32703) to all upstream peers TWO times. |
| 32703:30003 | Prepend IFN’s AS (32703) to all upstream peers THREE times. |
| 32703:30101 | Prepend IFN’s AS (32703) to Level3 ONE time. |
| 32703:30102 | Prepend IFN’s AS (32703) to Level3 TWO times. |
| 32703:30103 | Prepend IFN’s AS (32703) to Level3 THREE times. |
| 32703:30201 | Prepend IFN’s AS (32703) to Cogent ONE time. |
| 32703:30202 | Prepend IFN’s AS (32703) to Cogent TWO times. |
| 32703:30203 | Prepend IFN’s AS (32703) to Cogent THREE times. |
| 32703:20000 | Do not advertise prefixes to ANY peers |
| 32703:20003 | Do not advertise prefix to Cogent |
| 32703:20002 | Do no advertise prefix to Level3 |
You may advertise any of your prefixes as long as they are a /24 or smaller.